Solidigm™ DC-P4510 Product Brief
Formerly Intel® SSD DC-P4510 Series
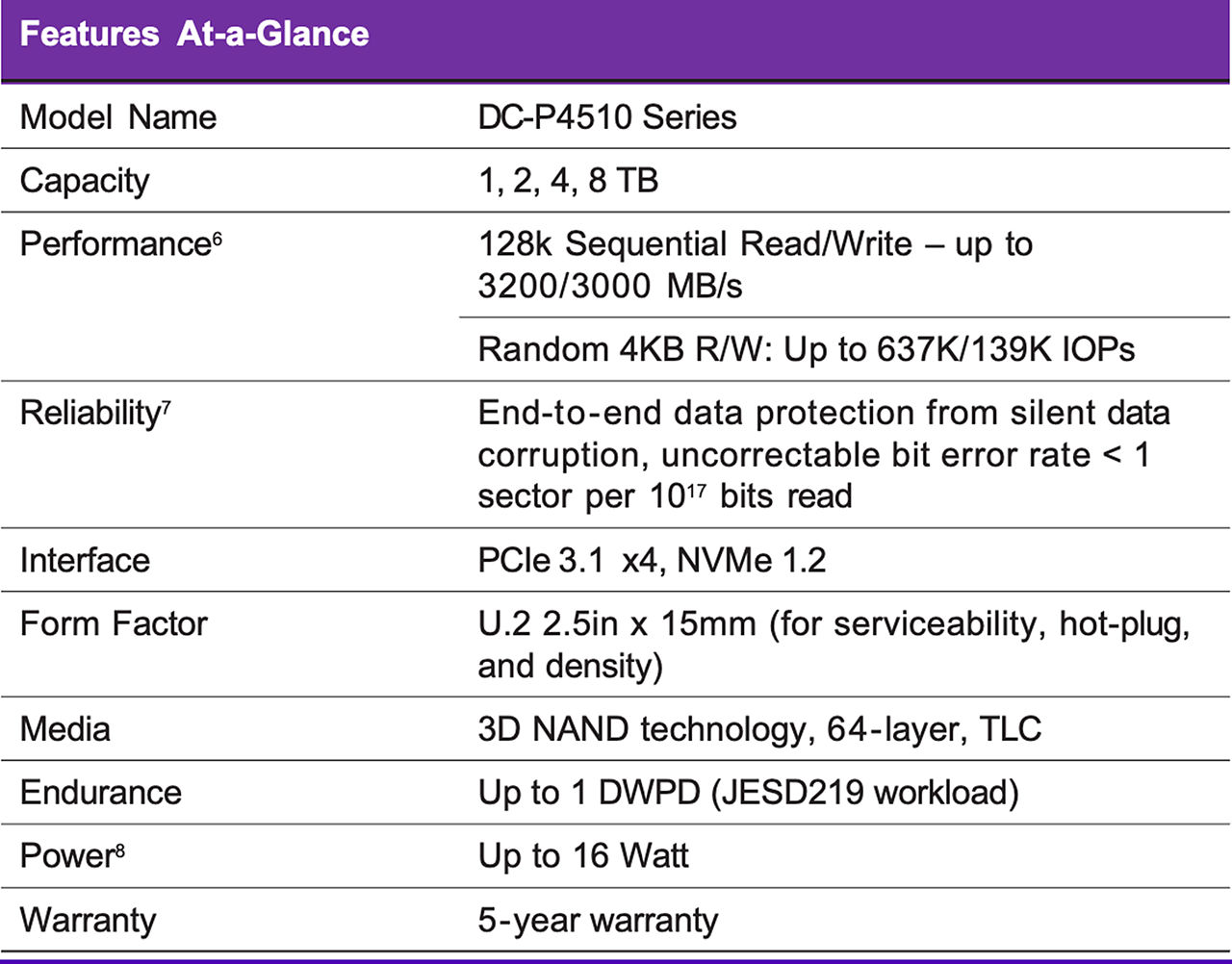
Built from the success of its cloud-inspired predecessor, the Solidigm DC-P4500 Series, and architected with 64-layer, TLC, 3D NAND technology, the Solidigm™ DC-P4510 Series delivers performance, Quality of Service (QoS), and capacity improvements to further optimize storage efficiency, enabling data centers to do more per server, minimize service disruptions, and efficiently manage at scale. Built on NVMe specification 1.2, these PCIe SSDs are available in 1TB, 2TB, 4TB, and 8TB in the U.2 2.5” (15mm) form factor.

An SSD built for cloud storage architectures
Multi-cloud has become a core element for any enterprise strategy, and top cloud providers have responded by openly embracing PCIe/NVMe-based SSDs with scalable performance, low latency, and continued innovation.
As software-defined and converged infrastructures are swiftly adopted, the need increases to maximize efficiency, revitalize existing hardware, deploy new workloads, and yet reduce operational expenditures.
The Solidigm DC-P4510 Series meets these requirements. It significantly increases server agility and utilization, and accelerates applications across a wide range of cloud workloads.
Do more per server
Solidigm’s 64-layer, TLC, 3D NAND technology enables the DC-P4510 to double the capacity available compared to its immediate predecessor, the Solidigm DC-P4500. This increased density is the key to supporting broader workloads, allowing cloud service providers to increase users and improve data service levels. Better QoS is ensured with an intelligent firmware algorithm that keeps host and background data read/write at an optimum balance.
With the DC-P4510, host applications will not only have access to double the capacity, but will also be serviced at up to 80% faster write rate, [1] up to 2x better random write IOPS/TB, [2] and up to 10x reduction of service time (compared to the DC-P4500) at a QoS metric of 99.99% availability for random access workload. [3] With this level of workload ability and agility, data centers can refresh existing hardware and reduce operational expenditures.
Minimize service disruptions
To ensure telemetry information without disrupting ongoing I/Os, the DC-P4510 includes enhanced SMART monitoring of drive health and status, using an in-band mechanism and out-of-band access. A power loss imminent (PLI) protection scheme with a built-in self-test guards against data loss if system power is suddenly cut.
Coupled with our industry-leading end-to-end data path protection scheme, [7] PLI features enable ease of deployment into resilient data centers where data corruption from system-level glitches is not tolerated. The DC-P4510 combines firmware enhancements with new 3D NAND features to prioritize host workload and ensure better service levels. The result: 6x workload support at a given service level response time. [4]
Efficiently manage at scale [5]
To help data centers make the most of increased SSD capacity per server, dynamic namespace management delivers the flexibility to enable more users and scale deployment. The DC-P4510 also provides security features like TCG Opal* 2.0 and built-in AES-XTS 256-bit encryption engine, required by some secure platforms.
With the capability to manage multiple firmware versions on a drive and to support updates without a reset, the DC-P4510 improves integration and increases the ease and efficiency of deploying at scale.
Choose the DC-P4510 for data center storage
With the increased density of Solidigm 64-layer 3D NAND and enhanced firmware features, the DC-P4510 is built to handle read-intensive workloads and beyond. The DC-P4510 creates greater Quality of Service, bandwidth, and performance to lead data centers through their evolving transformation. [1,2,3]
Notes
[1] Solidigm test: Comparing 128KB Sequential Write Bandwidth at queue depth 128, between SolidigmDC-P45100 Series 2TB and Solidigm DC P4500 Series 2TB. FIO* uses the configuration listed in footnote 6.
[2] Solidigm test: Comparing 4KB Random Write IOPS at queue depth 128, between SolidigmDC-P4510 Series 2TB and Solidigm DC P4500 Series 2TB. FIO* uses the configuration listed in footnote 6.
[3] Solidigm test: Comparing 4KB Random Read queue depth 1 latency at 99.99% percentile, between SolidigmDC-P4510 Series 2TB and Solidigm DC P4500 Series 2TB. FIO* uses the configuration listed in footnote 6.
[4] Solidigm test: Comparing SolidigmDC-P4510 Series 2TB, Solidigm DC P4500 Series 2TB under Aerospike Certification test. P4510 and P4500 can sustain 48x and 8x the workload respectively, meeting the certification requirement. Requirement is to maintain 95% of IO completion within 1msec. The Aerospike Certification Test (ACT) shows latency responses when reading from and writing to a database concurrently. Through a combination of large (128K) block reads and writes and small (1.5K) block reads, it simulates real world database workloads. For example, a 1x workload is 2000 reads/ second and 1000 writes/second; a 3x workload is 6000 reads/second and 3000 writes.
[5] All manageability features are not available at the time of the product release but will be available in future maintenance release. Please refer to product specification for details about feature description and availability.
[6] FIO* was used with this configuration: Intel® Server Board S2600WTTR, Intel® Xeon® E5-2699 v4, Speed: 2.30GHz, Intel BIOS: Internal Release, DRAM: DDR4 – 32GB, OS: Linux* Centos* 7.2 kernel 4.8.6. SSD firmware version VDV10120. Testing performed by Intel.
[7] Source - Solidigm. End-to-end data protection refers to the set of methods used to detect and correct the integrity of data across the full path as it is read or written between the host and the SSD controller and media. Claim is based on average of Solidigm drive error rates vs. average of competitor drive error rates. Neutron radiation is used to determine silent data corruption rates and as a measure of overall end-to-end data protection effectiveness. Silent errors were measured at run-time and at post-reboot after a drive “hang” by comparing expected data vs actual data returned by drive. The annual rate of data corruption was projected from the rate during accelerated testing divided by the acceleration of the beam (see JEDEC standard JESD89A).
[8] Average power measured by Sequential Write workload with transfer size of 128KB and queue depth of 128. FIO* uses the configuration listed in footnote 6.
Solidigm technologies’ features and benefits depend on system configuration and may require enabled hardware, software, or service activation. Performance varies depending on system configuration. No computer system can be absolutely secure. Check with your system manufacturer or retailer to learn more.
Solidigm disclaims all express and implied warranties, including without limitation the implied warranties of merchantability, fitness for a particular purpose, and non-infringement, as well as any warranty arising from course of performance, course of dealing, or usage in trade.
Benchmark results were obtained prior to implementation of recent software patches and firmware updates intended to address exploits referred to as “Spectre” and “Meltdown”. Implementation of these updates may make these results inapplicable to your device or system.
Software and workloads used in performance tests may have been optimized for performance only on Solidigm drives.
Tests document performance of components on a particular test, in specific systems. Differences in hardware, software, or configuration will affect actual performance. Consult other sources of information to evaluate performance as you consider your purchase.
Solidigm, and the Solidigm logo are trademarks of Solidigm Corporation in the U.S. and/or other countries.
*Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.