Solidigm™ D7-P5520 and D7-P5620 Product Brief
The industry’s most advanced PCIe 4.0 portfolio. [1] Performance-tuned for the real world.
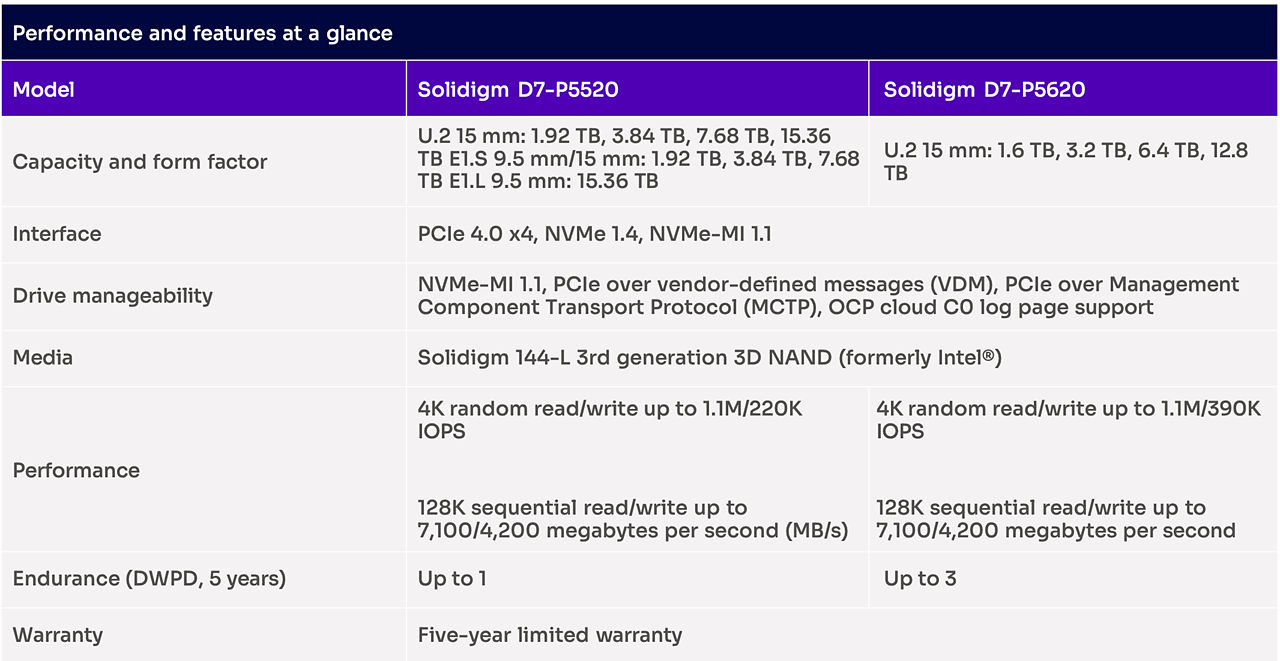
Our broadest and highest-performing family of TLC 3D NAND SSDs, Solidigm™ D7-P5520 and Solidigm™ D7-P5620 drives (formerly Intel®), are the latest addition to the performance-optimized D7 series. These drives provide standard endurance and medium endurance, respectively, across an extended range of capacities and form factors.

Building from multiple generations of PCIe 4.0 and deep industry insight, this is the industry’s most advanced PCIe 4.0 portfolio with performance tuned for real-world applications. They efficiently accelerate compute and storage workloads in cloud and enterprise across a breadth of 1U and 2U server configurations. Designed and tested with zero tolerance for data errors [2] and consistently durable performance, [3] they can be deployed with the utmost confidence.
TLC 3D NAND SSD series highlights
Compared to the previous generation of PCIe 4.0 products, performance has been significantly boosted across the board, enabling workload acceleration in mixed and read-intensive applications.
Read intensive

Write intensive
Form factor and capacity expansion enable server modernization opportunities spanning a broad range of 1U and 2U
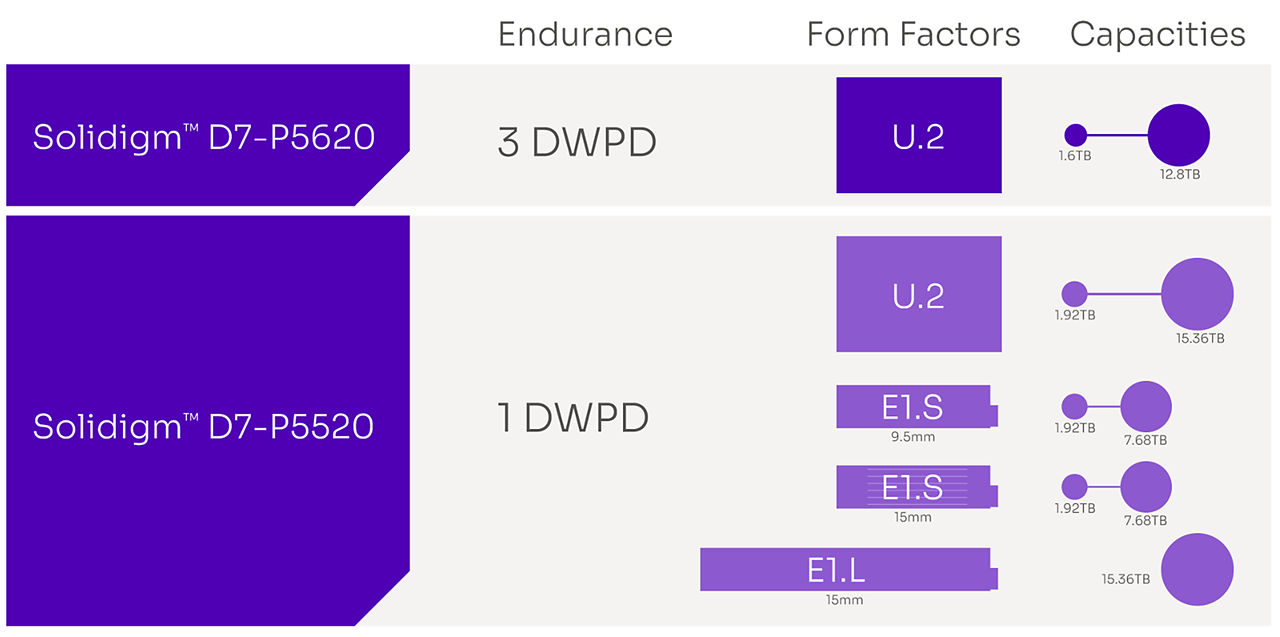
With NAND media, firmware, and controllers common to all SKUs in the family, customers have an opportunity to ease qualifications across form factors and capacities, given the possibility of data sharing.
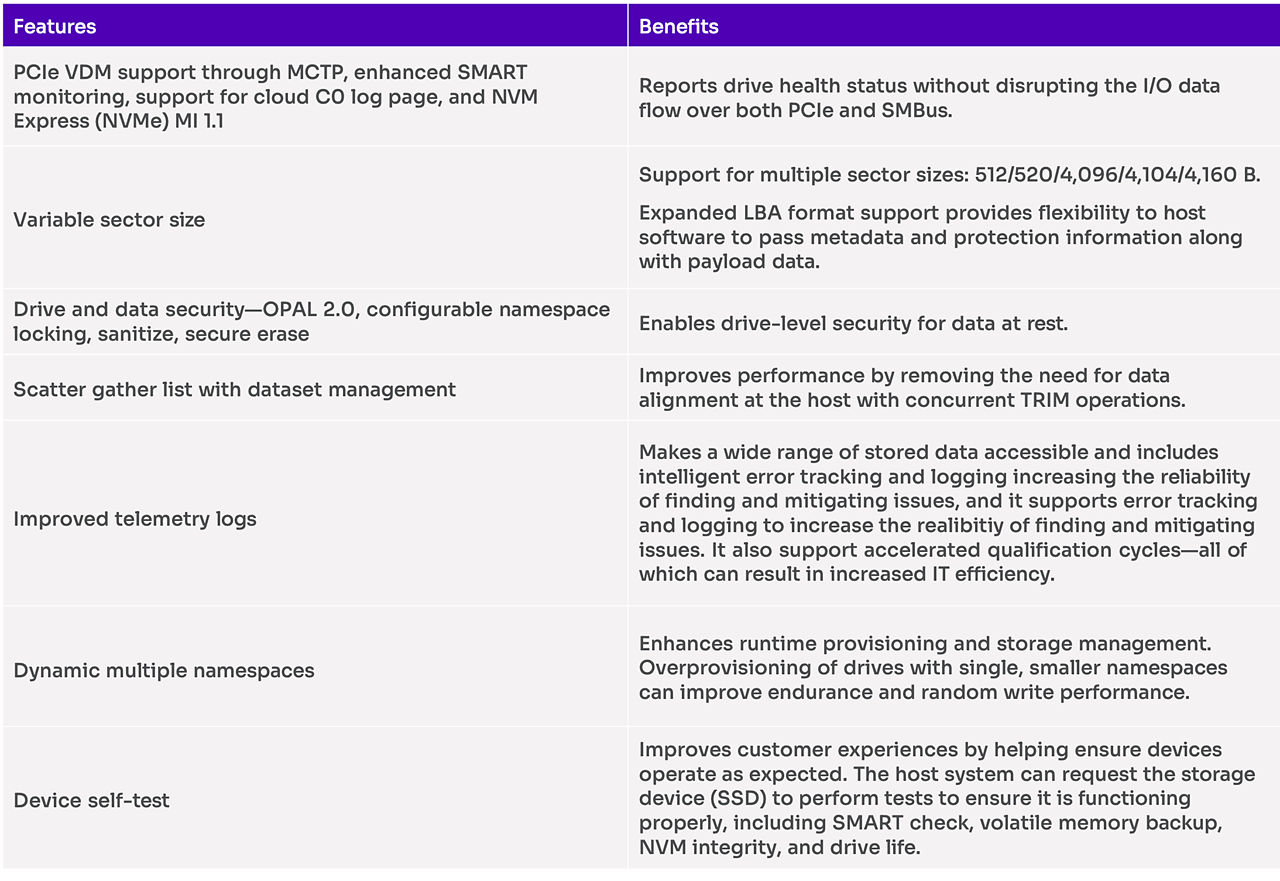
Advanced feature set
Building on our previous generation PCIe 4.0 data center SSDs, the Solidigm D7-P5520 and D7-P5620 offer a wide range of new features (in addition to features supported by the Solidigm D7-P5510) that are essential to building modern data centers. Some of the notable drive features include:
Optimized for real-world cloud and enterprise storage workloads
Overall performance improvements combined with our deep, industry-wide technical insight deliver performance tuned for the real world, helping to efficiently accelerate compute and storage workloads for cloud and enterprise.
Examples of unlocking cloud storage workloads—Cloud compute services are used across a range of scenarios such as data backup, disaster recovery, databases, email, and virtual desktop. These usages present a highly random, mixed workload environment valuing low latency to improve the user experience, and the Solidigm D7-P5520 delivers nearly 11%6 better response time than prior-generation drives. Server-based storage solutions using virtualization software are another common cloud storage workload. VMs in these workloads create a mix of reads and writes that can be random or sequential. Compared to prior-generation drives, the Solidigm D7-P5520 accelerates these workloads with up to 13% better random read IOPS and up to 11% better sequential write throughput. [7]
Examples of unlocking enterprise storage workloads—As the name implies, general purpose servers (GPS) support a range of workloads that can span databases, email, unified communications, content delivery, and more. Given the nature of these servers, throughput and latency in a mixed environment is valued. Compared to the prior generation, the Solidigm SSD D7-P5520 accelerates 80/20 sequential/random read throughput up to 15% and reduces latency up to 13.5%. [8] Data pipelines serving advanced workloads such as big data, machine learning, and AI are increasingly deployed in enterprises. I/O patterns vary widely through the pipeline phases, and the Solidigm D7-P5520 delivers with up to 7 % better throughput for data- ingestion workloads, up to 6.7% read latency improvement in a 50/50 workload for data preparation, and up to 23.7% higher random read IOPS for training workloads compared to the prior generation. [9]
TCO savings opportunities
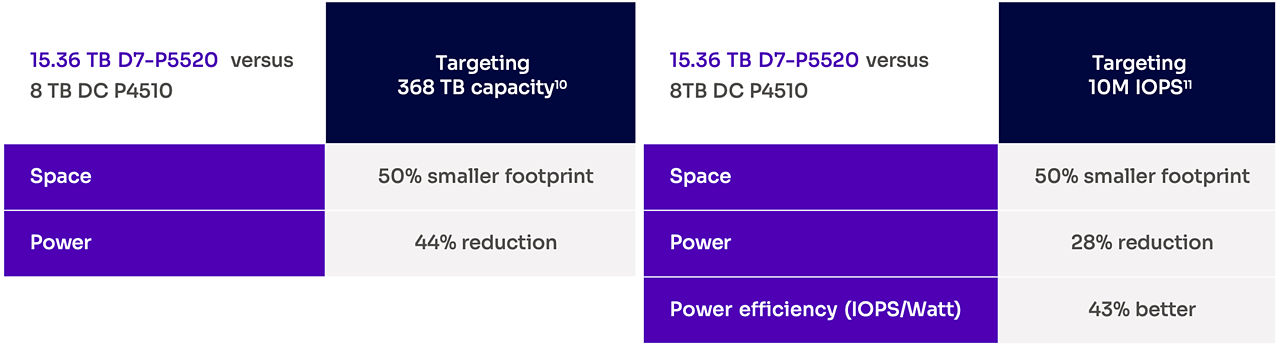
Whether solving for storage-footprint optimization or for performance density, expanded capacity ranges and accelerated performance enable a range of cost-saving opportunities.
2U server examples
Deploy with confidence
Solidigm D7-P5520 and Solidigm D7-P5620 drives are designed and tested with a passion for—and a relentless focus on—quality, reliability, and consistency, so you can deploy them with confidence.
Quality and reliability designed into every drive:
- In-house design or design control of all critical components
- Robust third-party component quality assurance (QA) program
- Enhanced Power Loss Management firmware checks to ensure data accuracy [12]
Drives validated and tested above and beyond:
- Data reliability: Data reliability is enhanced on multiple levels with PLI testing that simulates real-world conditions, UBER testing to 10x beyond JEDEC specification, and SDC testing at the highest levels in the industry.2
- Drive reliability: Proven reliability delivers AFR significantly better than JEDEC in high-volume manufacturing. [13] Robust RDT and margin-corner testing helps ensure drives perform reliably in real-world conditions.
- Consistency: Up to 90% IOPS consistency and <0.3% IOPS variability provides consistent performance over life of the drive [3]
To learn more about how Solidigm D7-P5520 and Solidigm D7-P5620 drives can help you unlock the value of your data, visit our value calculator at: Solidigm.com.
Notes
[1] Comparing Solidigm™ D7-P5520 to key competitors where Solidigm is the only supplier offering E1.L and co-leads U.2 and E1.S capacity ranges. Also factors in read responsiveness under write pressure comparing D7-P5520 and similar competitor drive using Intel® Server Board M50CYP2SB2U, Intel® ICE LAKE - P5 4GXRAV D, Number of CPUs: 2, Number of Cores: 36, DRAM: DDR4 – 64GB, OS: CentOS Linux release 7.5.1804, Kernel Version: 3.10.0-862.el7.x86_64 using FIO for workload measurement. Other factors considered are the additional measures implemented by Solidigm in designing in for quality and reliability and product testing (see footnotes 2 and 12).
[2] SDC modeling and testing: Solidigm drives are tested to 1E-17 under a full range of conditions and cycle counts throughout the life of the drive, which is 10x higher than 1E-16 specified in JEDEC Solid State Drive Requirements and Endurance Test Method (JESD218) (see jedec.org/standards-documents/focus/flash/solid-state-drives). RD: Typical reliability demonstration test involve 1K drives for 1K hours to levels down to 1E-18. Solidigm drives are tested at the neutron source at Los Alamos National Labs to measure SDC susceptibility to 1E-23 with modeling to 1E-25. In three generations of testing at Los Alamos, equivalent to more than 5M hours of operational use, zero SDC errors have been detected on Solidigm drives, and no evidence of other suppliers testing at the facility has been observed.
[3] Solidigm™ D7-P5520 and D7-P5620 product spec for IOPS consistency. IOPS variability measured after adjusting SSD cycle limit to simulate end of life behavior. Results are estimated or simulated.
[4] Comparing product specs of the 3.84 TB Solidigm SSD D7-P5520 with 130 µs four-nines latency and 1,000K/200K random read/write IOPS to 3.84 TB Solidigm SSD D7-P5510 with 230 µs four-nines latency and 700K/170K random read/write IOPS. Test and system configuration: Intel® Xeon® Gold 6254 processor at 3.10 GHz, 24.75 MB, 200 W, 18 cores, BIOS: SE5C620.86B.02.01.0011.032620200659, 2 CPU sockets, 32 GB RAM capacity, DDR4 RAM model, RAM stuffing: N/A, two DIMM slots populated, PCIe attach: CPU (not PCH lane attach), chipset: Intel C610 Chipset, switch/retimer model/vendor: Intel A2U44X25NVMEDK, NVMe driver: Inbox, C-states: disabled, Intel Hyper-Threading Technology (Intel HT Technology): disabled, CPU governor (through OS): performance mode, OS: CentOS 8.2.2004, kernel: 5.4.49 fio tool used for I/O data.
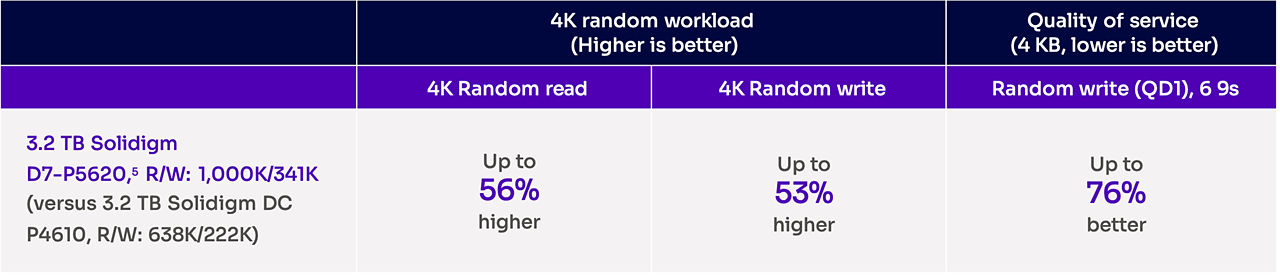
[5] Comparing product specs of the 3.2TB Solidigm D7-P5620 with 1000K/341K Random R/W IOPS to 3.2TB Solidigm D7-P4610 with 638K/222K Random R/W IOPS. Latency for the two drives measured was 137usec and 586usec respectively on 6 9s latency for 100% QD1 random write IO.Test and System Configuration: Intel® Xeon® Gold 6254 CPU @ 3.10GHz 24.75MB 200W 18 cores, BIOS: SE5C620.86B.02.01.0011.032620200659, CPU Sockets: 2, RAM Capacity: 32GB, RAM Model: DDR4, RAM Stuffing: N/A, DIMM Slots Populated: Slot(s): 2, PCIe Attach: CPU (not PCH lane attach), Chipset: Intel® C610 Chipset , Switch/ReTimer Model/Vendor: Intel A2U44X25NVMEDK, NVMe Driver: Inbox, C-states: Disabled, Hyper Threading: Disabled, CPU Governor (through OS): Performance Mode, OS: CentOS 8.2.2004, Kernel: 5.4.49 FIO tool used for IO data.
[6] Workload I/O characteristics based on research of publicly available materials conducted by Solidigm. Comparing 7.68 TB Solidigm SSD D7-P5520 and Solidigm SSD D7-P5510. Measured results of BW 1,784 MB/s, 1,695 MB/s respectively and 181 µs and 203 µs latency, respectively. Transfer size of 8 KB with a QD32. Test and system configuration: Intel Server Board M50CYP2SB2U, Intel Ice Lake P5 4GXRAVD, two CPUs, 36 cores, 64 GB DDR4 DRAM, OS: CentOS Linux release 7.5.1804, kernel: 3.10.0- 862.el7.x86_64. I/O measured using fio tool.
[7] Workload I/O characteristics based on research of publicly available materials conducted by Solidigm. Comparing 7.68 TB Solidigm SSD D7-P5520 and Solidigm SSD D7-P5510. Measured results of 233.7 and 206 RR KIOPS respectively using 4 KB transfer size and QD16, and 4.4 and 4.0 SW GB/s respectively using 128 KB transfer size and QD8. Test and system configuration: Intel Server Board M50CYP2SB2U, Intel Ice Lake P5 4GXRAVD, two CPUs, 36 cores, 64 GB DDR4 DRAM, OS: CentOS Linux release 7.5.1804, kernel: 3.10.0-862.el7.x86_64. I/O measured using fio tool.
[8] Workload IO characteristics based on research of publicly available materials conducted by Solidigm. Comparing 7.68TB Solidigm D7-P5520 to Solidigm D7-P5510. Workload of 80/20 Sequential Read and Random read on two namespaces concurrently with 32KB transfer size and QD=32. Aggregate bandwidth measured of 6980, 6074 MB/sec and latency of 295, 341 usec for D7-P5520, D7-P5510, PM9A3 respectively. Test and System Configuration: Intel® Server Board S2600WFT, Intel® Xeon® Gold 6254, Speed: 3.1GHz, Number of CPUs: 2, Number of Cores: 36, DRAM: DDR4 – 32GB, OS: CentOS Linux release 7.5.1804, Kernel Version: 3.10.0-862.el7.x86_64, G4SAC Gen4 switch PCIe card with Microsemi switch. IO measured using FIO tool.
[9] Workload I/O characteristics based on research of publicly available materials conducted by Solidigm. Comparing 3.84 TB Solidigm SSD D7-P5520 and Solidigm SSD D7-P5510 with measured write throughput of 3,687 MB/s and 3,443 MB/s, random read/write throughput of 1,064 MB/s and 997 MB/s, and random read bandwidth of 1,691 MB/s and 1,367 MB/s, respectively. Test and system configuration: Intel Server Board S2600WFT, Intel Xeon Gold 6254 processor, 3.1 GHz, two CPUs, 36 cores, 32 GB DDR4 DRAM, OS: CentOS Linux release 7.5.1804, kernel: 3.10.0-862.el7.x86_64, G4SAC Gen4 switch PCIe card with Microsemi switch. For I/O workload measurement. I/O measured using fio tool.
[10] Comparing 48 x U.2 7.68 TB Solidigm SSD D7-P5510 and 24 x U.2 15.36 TB Solidigm SSD D7-P5520. Max average write power from product specifications.
[11] Comparing 3.84 TB Solidigm SSD D7-P5510 at 700K 4 KB RR IOPS and 15 W average active read power to 3.84 TB Solidigm SSD D7-P5520 at 1,000K 4 KB RR IOPS and 15 W average active read power. IOPS and active read power from product specifications.
[12] Designed-in an extra firmware check to validate that data was saved accurately upon power restoration
[13] Solidigm SSD D7-P5510 and Solidigm SSD D5-P5316 144-layer TLC/QLC AFR data from Q1 2021 through Q1 2022 used as a proxy for expected Solidigm SSD D7-P5520 and Solidigm SSD D7-P5620 AFR in high-volume manufacturing.
All information provided is subject to change at any time, without notice. Solidigm™ may make changes to manufacturing life cycle, specifications, and product descriptions at any time, without notice. The information herein is provided “as-is” and Solidigm does not make any representations or warranties whatsoever regarding accuracy of the information, nor on the product features, availability, functionality, or compatibility of the products listed. Please contact system vendor for more information on specific products or systems.
Performance results are based on testing as of dates shown in configurations and may not reflect all publicly available updates. See backup for configuration details. No product or component can be absolutely secure.
Performance varies by use, configuration and other factors.
Refer to the spec sheet for formal definitions of product properties and features.
Solidigm technologies may require enabled hardware, software or service activation. No product or component can be absolutely secure. Your costs and results may vary. Performance varies by use, configuration and other factors. Other names and brands may be claimed as property of others. See our complete legal Notices and Disclaimers. Solidigm is committed to respecting human rights and avoiding complicity in human rights abuses. Solidigm products and software are intended only to be used in applications that do not cause or contribute to a violation of an internationally recognized human right.
Solidigm and the Solidigm logo are trademarks of Solidigm. Intel is a registered trademark of Intel Corporation. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
© Solidigm 2022. All rights reserved.